Effective Ways to Manage Hypoglycemia Diet for Better Blood Sugar Control in 2025
Managing a hypoglycemia diet is crucial for individuals looking to maintain stable blood sugar levels. With the increasing prevalence of low blood sugar conditions in our society today, it’s essential to understand not only what foods can help stabilize blood sugar but also how to construct an effective dietary plan for hypoglycemia. This article will provide in-depth insights into managing low blood sugar through nutrition, the importance of meal planning, and practical tips for enforcing dietary changes.
Understanding Hypoglycemia
Before diving into dietary recommendations, it’s essential to understand what hypoglycemia is. Hypoglycemia occurs when blood sugar levels drop below the normal range of roughly 70 mg/dL. Symptoms can include shakiness, sweating, dizziness, and sudden fatigue. Recognizing these signs is the first step to managing your blood sugar levels effectively.
Symptoms of Hypoglycemia
Being aware of the symptoms of hypoglycemia can help you manage this condition proactively. Common symptoms include irritability, confusion, rapid heartbeat, and in severe cases, loss of consciousness. Keeping a hypoglycemia symptom diary can assist in recognizing patterns and triggers. This awareness will help you take precautionary measures in your dietary planning and meal timing for hypoglycemia.
Common Triggers for Low Blood Sugar
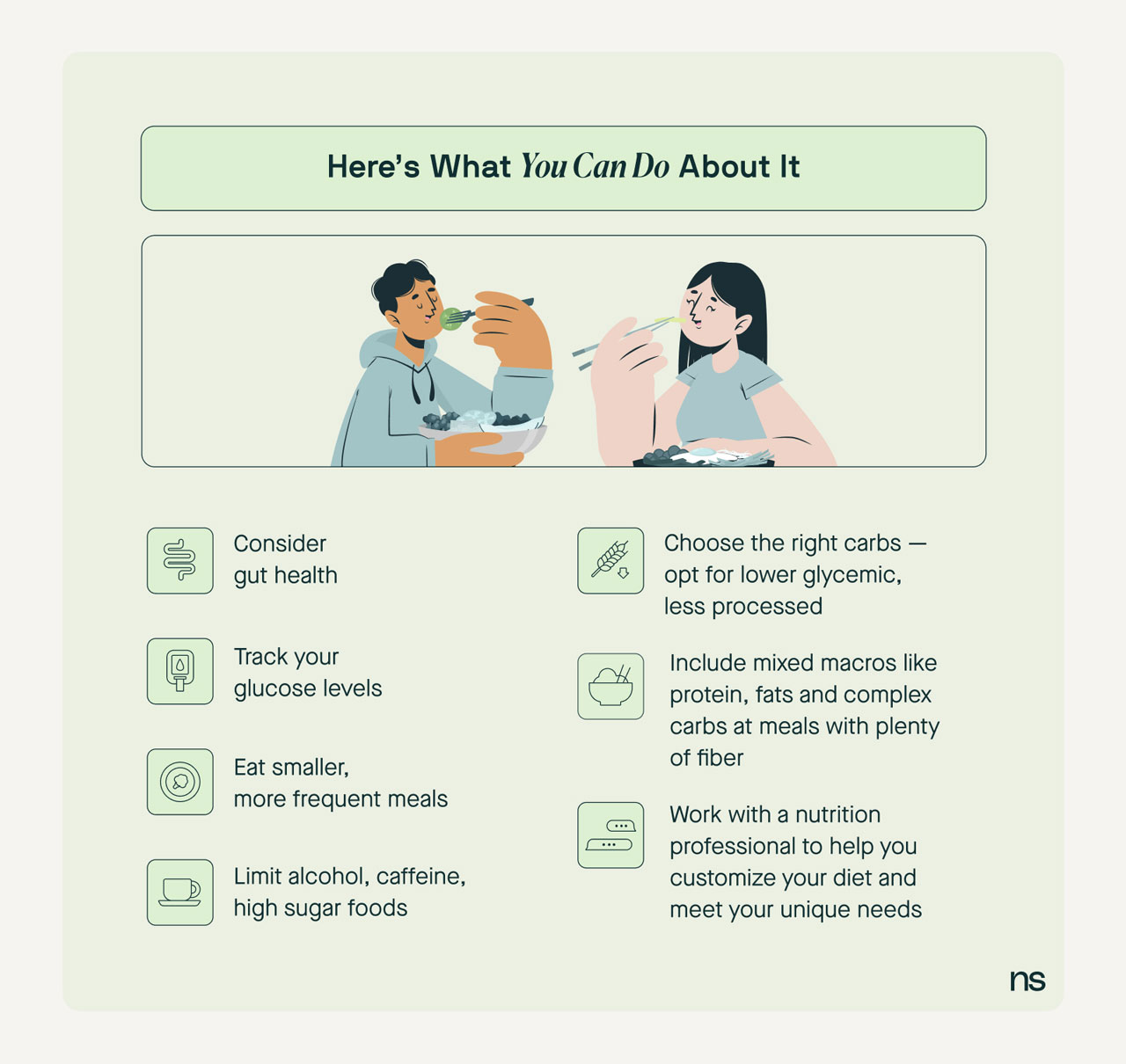
Various factors can trigger low blood sugar levels, including skipping meals, excessive alcohol consumption, or over-exercising without proper fuel. Understanding these triggers is crucial as it provides context for creating a tailored hypoglycemia meal plan. It’s advised to consume small, balanced meals throughout the day to minimize the risk of a sugar crash and support stable blood sugar levels.
Building a Balanced Hypoglycemia Diet
A successful low blood sugar diet focuses on incorporating nutrient-rich foods that prevent spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels. The key components include complex carbohydrates, protein-rich foods, and plenty of fiber. Integrating these foods helps support glucose stability, which is essential for individuals who are prone to hypoglycemia.
Foods to Include in Your Hypoglycemia Diet
When planning meals, the best foods for hypoglycemia include whole grains, legumes, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Complex carbohydrates help slow sugar absorption into the bloodstream, for example, whole oats or brown rice. In addition, fiber-rich foods such as vegetables and whole grains can stabilize blood sugar and improve digestive health. Let’s look at some examples:
- Quinoa, a good source of complex carbohydrates and protein.
- Chickpeas, high in fiber and easy to incorporate in salads and soups.
- Nuts and seeds, which offer beneficial fats and protein.
Simple Meal Ideas for Hypoglycemia
When constructing meals, practicality also plays a key role. Examples of balanced meals for hypoglycemia may include a quinoa salad with chickpeas, mixed vegetables, and a light vinaigrette dressing. Snacks can include a piece of fruit paired with a handful of nuts. Such combinations not only satisfy the appetite but also help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Portion Control for Hypoglycemia
Portion control is another essential factor in managing low blood sugar. Using small plates can help reduce portion sizes without feeling deprived. Eating balanced meals every 3-4 hours can also prevent sugar crashes. Remember to monitor portion sizes of high glycemic foods to combat sudden spikes in blood sugar.
Integrating Meal Timing and Prepping
Alongside food choices, when you eat is equally critical for monitoring blood sugar. Establishing regular meal times can prevent the risks associated with spikes and dips in blood sugar levels. Recommended meal frequency often suggests eating small meals and snacks every 2-3 hours. This meal frequency helps not only stabilize blood sugar but also keeps energy levels consistent.
Meal Prepping for Hypoglycemia
Meal prepping is a practical strategy for avoiding food-related pitfalls. Prepping meals on weekends or designated days allows individuals to control portion sizes better and ensure healthy snacks for low blood sugar are readily available. Preparing easy recipes can include things like grilled chicken with steamed vegetables or overnight oats for breakfast. Prioritizing simple, low sugar recipes ensures quick access to a nutritious meal whenever necessary.
Optimal Snacking Strategies
Having healthy snacks on hand can make all the difference in managing cravings and maintaining steady energy levels. Portable options like carrot sticks with hummus, Greek yogurt, or protein bars provide quick, on-the-go nutrients that can help prevent low blood sugar levels. Thoughtful snacking plays a big role in avoiding sugar spikes and maintaining stable energy throughout the day.
Importance of Breakfast for Blood Sugar Management
Breakfast should not be skipped, as it’s crucial for providing the fuel your body needs after a night’s rest. Include a source of protein, a complex carbohydrate, and some healthy fat to promote a balanced start to your day. Great options include eggs with whole grain toast or a smoothie with spinach, banana, and almond butter. Emphasizing the importance of breakfast will help improve your overall nutrient intake and blood sugar regulation.
Adjusting Lifestyle for Better Control
An effective hypoglycemia management plan extends beyond just dietary choices. Making lifestyle adjustments can significantly affect blood sugar levels. Regular exercise, adequate hydration, and adequate sleep all contribute to optimal management of blood sugar levels. Developing a set routine helps reinforce these positive habits over time.
Hydration and Blood Sugar Levels
Staying hydrated is vital in managing hypoglycemia. Dehydration can impede your body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water daily. Additionally, incorporating drinks for low blood sugar, such as herbal teas or infused water with lemon, can help maintain proper hydration and balance.
Stress and Its Impact on Blood Sugar
Stress can profoundly affect blood sugar, often leading to fluctuations. Implement stress-reducing techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, or light exercises like yoga. These techniques not only help improve emotional well-being but are also vital for effective blood sugar management.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Regularly
Regularly checking your blood sugar levels enables you to manage hypoglycemia more effectively. Whether you use a blood glucose meter or continuous glucose monitoring, keeping track of fluctuations will aid in adjusting your dietary habits and lifestyle choices for optimal control.
Key Takeaways
- Implement a balanced hypoglycemia diet focusing on complex carbohydrates, proteins, and fiber.
- Establish consistent meal times and incorporate easy meal prepping techniques.
- Stay hydrated and actively manage stress to support stable blood sugar levels.
- Regularly monitor blood sugar to better understand effects and triggers.
- Nutrition education and planning can significantly improve overall health and energy levels.
FAQ
1. What are the best foods for hypoglycemia?
The best foods for hypoglycemia typically include complex carbohydrates, protein-rich foods, and healthy fats. Popular selections, such as oats, legumes, and avocados, provide essential nutrients that help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
2. How can I create a meal plan for hypoglycemia?
To create an effective dietary plan for hypoglycemia, include a variety of nutrient-dense foods. Focus on portion sizes, planning meals every 3 hours, and including snacks comprised of proteins and fibers. This approach supports consistent blood sugar levels.
3. What should I avoid in my hypoglycemia diet?
Avoiding foods high in refined sugars and processed items is important in addressing hypoglycemia. This also includes certain simple carbohydrates that can cause a spike in blood sugar, followed by a rapid drop.
4. Are there any vitamin supplements that can help with hypoglycemia?
Vitamin B, particularly B6, and magnesium supplements may aid in blood sugar regulation. Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations based on your specific health needs.
5. How does meal timing affect blood sugar levels?
Meal timing plays a critical role in hypoglycemia management. Eating regular meals and snacks prevents dips in blood sugar, ensuring a steady source of energy. Consider meal prepping to facilitate timely nutrient intake.
6. Can hydration influence my blood sugar levels?
Yes, adequate hydration is essential for managing low blood sugar. Dehydration can lead to impaired glucose regulation, making it important to drink sufficient water and hydrating beverages.
7. What role do healthy snacks play in managing low blood sugar?
Healthy snacks between meals can keep blood sugar levels stable and curb cravings. Snack options should ideally include a combination of proteins and healthy fats to effectively maintain energy and prevent drops in glucose levels.