“`html
Best 7 Practical Solutions for Managing Irritable Bowel Syndrome with a High Fiber Diet in 2025
Managing irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is crucial for maintaining digestive health, especially when incorporating a high fiber diet. Fiber can ease symptoms like bloating, constipation, and cramping by improving overall gut function. This article presents seven practical solutions tailored to managing IBS through dietary fiber and mindful eating practices in 2025.
The Importance of Dietary Fiber for IBS
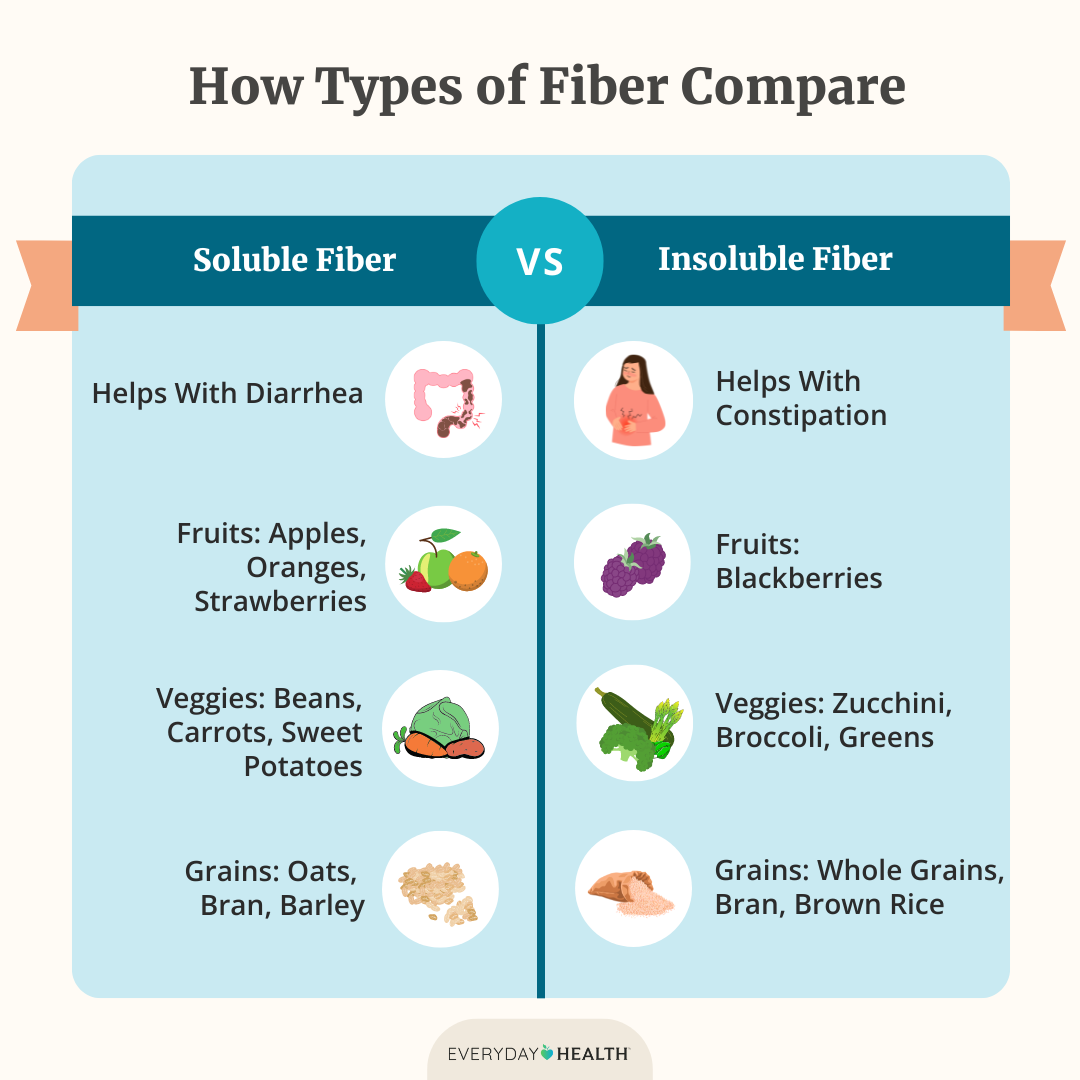
The intake of dietary fiber plays a vital role in promoting a healthy gut and managing IBS symptoms. Fiber helps in regulating bowel movements and can alleviate common issues like constipation relief and bloating management. While there are two primary types of fiber, soluble fiber, found in oats and beans, helps to soften stool, whereas insoluble fiber, found in whole grains, promotes movement in the digestive tract. Following a high-fiber diet can effectively manage symptoms and improve gut health.
Understanding Fiber Types: Soluble vs. Insoluble
When considering a high fiber diet for IBS, it is essential to understand the difference between soluble fiber and insoluble fiber. Soluble fiber dissolves in water and forms a gel-like substance, slowing down digestion and potentially aiding in IBS management. Foods high in soluble fiber include psyllium husk, oats, and certain fruits. Conversely, insoluble fiber adds bulk to the stool and aids in quicker excretion, which can benefit those experiencing constipation. Incorporating both types of fiber into your daily diet can enhance digestive health.
Daily Fiber Intake Goals for IBS Management
For adults, the recommended daily fiber goal is about 25-30 grams per day. However, individuals with IBS may need to tailor this intake based on their unique symptoms and dietary needs. Gradually increasing fiber intake rather than sudden changes can prevent exacerbating IBS flare-ups. Keeping a food journal can also help track fiber consumption and identify any trigger foods that may lead to discomfort, thus facilitating effective meal planning.
Incorporating High Fiber Foods into Your Diet
Integrating a variety of fiber-rich foods is essential for managing IBS. Focus on whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, which not only provide fiber but also essential vitamins. Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are excellent protein sources, while whole grains such as quinoa and brown rice can improve your overall nutrient profile. Consider easy meal options, like smoothies loaded with fruits and spinach, which offer a significant dose of dietary fiber while remaining gentle on the digestive system.
Low FODMAP Diet: A Practical Approach
Many individuals with IBS benefit from the low FODMAP diet, designed to minimize certain types of fermentable fibers known to cause digestive distress. In 2025, this diet continues to be a popular choice for managing IBS. Foods like garlic, onions, and certain dairy products are typically limited. Instead, focus on compliant foods such as bananas, strawberries, and gluten-free pasta, ensuring you still meet your daily fiber goal without the discomfort from high-FODMAP options.
Timing and Frequency of Meals for Optimal Digestive Health
For those managing IBS, meal timing and frequency can significantly impact gut health. Eating smaller, more frequent meals rather than three large ones can ease the digestive burden and help prevent sudden IBS flare-ups. Prioritize hydration as well; increase water intake when consuming more fiber to help aid digestion and prevent constipation.
Adopting a Balanced and Mindful Eating Strategy
In addition to a high-fiber diet, adopting a holistic approach that encompasses various lifestyle changes can enhance IBS management. Mindful eating techniques promote better digestion and help control portions. Listening to your body’s hunger signals and eating slowly can prevent overeating and increase the enjoyment of meals, resulting in a better overall eating experience.
Avoiding Trigger Foods: Nutrition Education and Meal Planning
Identifying and avoiding trigger foods is central to managing IBS symptoms. Common triggers include dairy products, caffeine, and fatty foods. With the help of a dietitian, track your food intake and symptoms, compiling a tailored list of foods to enjoy and ones to avoid. This practice forms an important part of successful meal planning and optimizing nutrition for IBS.
Exploring Probiotics and Prebiotics
Adding probiotics and prebiotics to your diet can be beneficial in promoting a healthy gut microbiome. Probiotic-rich foods such as yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables can help restore balance to gut flora while prebiotics found in garlic, onions, and asparagus feed beneficial gut bacteria. Together, these components can enhance digestive health and improve overall IBS management.
Key Takeaways
- Incorporate a mix of soluble and insoluble fiber into your daily diet to improve digestive health and alleviate IBS symptoms.
- Monitor daily fiber intake and consider table recording symptoms to identify and avoid trigger foods effectively.
- Use meal planning strategies that include high-fiber meals enriched with low FODMAP options, if necessary.
- Adopt mindful eating practices and proper meal timing to further support good digestive health.
- Consider adding probiotics and prebiotics to your diet to enhance gut health.
FAQ
1. What are the best fiber sources for IBS?
Optimal fiber sources for IBS include fiber-rich foods such as bananas, oats, and carrots for soluble fiber, along with whole grains, nuts, and seeds for insoluble fiber. Incorporating a mix of these can help manage symptoms effectively.
2. How can hydration help with IBS symptoms?
Staying adequately hydrated is essential, especially when consuming more dietary fiber. Increased fluid intake supports digestion, helps prevent constipation, and can minimize bloating, enhancing overall IBS management.
3. Can a dietitian help with managing IBS?
Absolutely! Consulting a dietitian provides personalized advice on nutrition for IBS, guidance on meal planning, and help in identifying trigger foods while tailoring the diet to your preferences and challenges.
4. What role does stress play in IBS?
Stress can significantly affect IBS symptoms. Implementing lifestyle changes, such as mindfulness practices and stress management techniques, should be part of managing digestive health and can help reduce flare-ups.
5. Are there specific meal suggestions for a high fiber diet?
Yes, meals such as overnight oats topped with fruits, salads with quinoa and vegetables, and soups made with lentils can be excellent high fiber recipes suitable for optimizing IBS management.
“`
