Effective Ways to Optimize Coyote Diet for Better Wildlife Management in 2025
Understanding Coyote Diet and Its Importance
The optimization of the **coyote diet** is crucial for effective wildlife management strategies in 2025. Recognizing what **coyotes eat** helps inform conservation efforts and coyote population management. **Coyote feeding habits** vary significantly based on the local environment, prey availability, and seasonal changes. A comprehensive understanding of a coyote’s *dietary needs* will enable wildlife managers to make informed decisions about habitat preservation and the interacting dynamics between **coyotes and their prey**. Coyote nutrition includes both *natural prey*, such as small mammals and birds, and opportunistic human-sourced foods, reflecting their **omnivorous behavior**.
What Do Coyotes Eat? An Overview
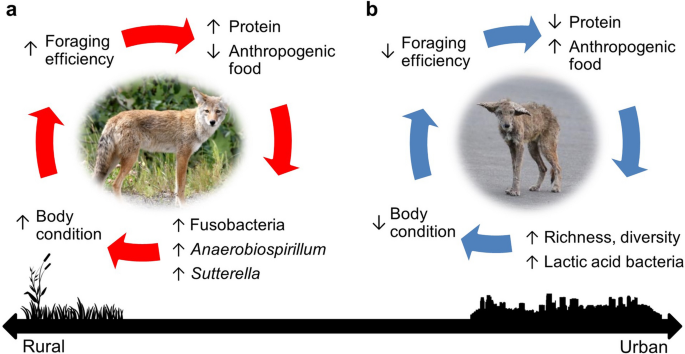
Coyotes are known for their **omnivorous diet**, characterized by versatility in their food choices. They primarily rely on small to medium-sized mammals like rodents, rabbits, and deer. Seasonal availability influences their **coyote prey** selection; for instance, during winter, they may target larger prey as smaller food sources become scarce. The **urban coyote diet** shifts to include more human-related food sources, emphasizing their adaptability. This dietary variety supports **coyote population dynamics** and overall health, impacting their reproduction and survival rates.
Types of Food Eaten by Coyotes
The **types of food eaten by coyotes** encompass both animal and plant sources. In urban areas, coyotes may scavenge on pet food, garbage, and human waste, showcasing their opportunistic feeding habits. Conversely, in rural locales, their diet primarily consists of natural prey. Studies indicate that assessing **coyote dietary preferences** is essential, as certain food sources contribute more to their health than others. **Coyote nutritional requirements** must be met to maintain optimal body condition, particularly during reproductive seasons or in times of stress like drought that impact prey availability.
Insights into Coyote Feeding Habits
Coyote eating habits play a fundamental role in the ecosystem, affecting both prey populations and the ecological balance. Understanding how *coyotes forage* helps in developing management techniques that can enhance wildlife conservation efforts. By observing their **coyote hunting strategies** and social structures, such as pack dynamics, wildlife managers can create effective management policies that promote healthy wildlife populations and mitigate human-coyote conflicts.
Coyote Scavenging Practices
**Coyote scavenging habits** are integral to their survival, particularly during food shortages. By consuming carrion, coyotes play a vital role in nutrient cycling within their ecosystem. This behavior also reflects their opportunistic nature. **Coyote carcass consumption** is beneficial for both their dietary needs and reduces the spread of disease by naturally recycling dead animal remains. Monitoring coyote behavior around *natural disasters or food shortages* can provide insights into the greater ecological impact of their scavenging.
The Impact of Diet on Coyote Health
The connection between **coyote diet** and health outcomes is profound. Research indicates that inadequate diets can lead to health deterioration, evident in the *body condition scores* of the population. Nutritionally rich food sources, such as rodents high in protein, ensure swift growth and reproductive success. Furthermore, understanding how **dietary fluctuations** due to environmental changes affect health can guide interventions when competitive species impact food availability. Recognizing **effects of diet on coyote health** could spur research to implement better management approaches.
Strategies for Improving Coyote Diet
Improving the **coyote dietary preferences** in specific territories enhances wildlife management. By focusing on the alignment of prey availability with coyote foraging behaviors, wildlife conservationists can strive for healthier coyote populations. Methods such as habitat enrichment and controlled prey monitoring facilitate optimal coyote feeding events. Adjusting land management practices can increase native prey populations, thereby indirectly benefitting coyote nutrition.
Enhancing Habitat for Optimal Feeding
Creating environments that support the **coyote prey** base—such as increasing populations of small mammals and birds—will directly benefit coyote health and adaptability. This approach requires collaboration with landowners to manage landscapes creatively. For instance, preserving natural grasslands allows for the growth of native flora that may support prey species. Increased prey **availability** means that the coyote’s **seasonal diet** can remain consistent and nutritionally balanced, supporting their **ecological impact** and role in the food chain.
Mitigating Human-Coyote Conflicts through Diet Management
Human-coyote interactions can escalate without effective management strategies surrounding coyote diet. By educating residents about minimizing food sources that attract coyotes and promoting coexistence strategies, conflicts can be decreased. For instance, discouraging outdoor pet food and securing trash can reduce **coyote competition for food items** and minimize encounters. Recognizing **coyote territorial feeding** behavioral traits can encourage communities to implement coexistence measures that respect both human and coyote needs.
Key Takeaways
- A well-rounded understanding of **coyote diet** leads to better management practices.
- Improving **availability** and maintaining dietary diversity are crucial for coyote health.
- Effective habitat management can enhance coyote prey populations.
- Educational outreach regarding human-coyote interactions can mitigate potential conflicts.
- Adaptable feeding habits help **coyotes thrive** in varying environments.
FAQ
1. What is the primary diet of coyotes?
The primary diet of coyotes mainly consists of small mammals, including rodents and rabbits. Additionally, **coyotes** engage in scavenging practices which can include leftover carrion, especially during food scarcity. Their **dietary preferences** shift depending on environmental conditions, availability of prey, and whether they are in urban or rural settings.
2. How do seasonal changes affect coyote dietary needs?
Seasonal changes significantly influence **coyote feeding patterns** and prey availability. During winter, coyotes may rely more on larger prey items, while spring and summer landscapes allow for a rebalance in their diet toward smaller mammals. The shift helps meet their *nutritional requirements* as they prepare for reproduction periods when energy demands increase.
3. What strategies can be implemented to improve coyote health and diet?
Improving coyote health and diet can be achieved through habitat enhancement to ensure healthy prey populations. Additionally, managing human-accessible food sources, restricting garbage availability, and community education will encourage coyotes to return to their natural prey-seeking behaviors instead of scavenging in urban settings.
4. Can urbanization negatively affect coyote diets?
Yes, urbanization can notably impact *coyote diets* by reducing natural prey sources and pushing them toward anthropogenic food, affecting their **health and behaviors**. Urban coyotes often become reliant on human waste and pet food, which can alter their **scavenging and hunting** habits, resulting in behavioral adaptations that can lead to conflicts.
5. How does dietary adaptability relate to coyote survival?
Dietary adaptability is crucial for coyote survival as it allows them to adjust to changing environmental conditions. Coyotes are opportunistic feeders with the ability to switch their diets based on availability, ensuring their population remains robust even in the face of prey decline or habitat disruption.